Satellite imagery has revolutionized the way scientists and researchers monitor the environment. The adoption of annotated satellite imagery has further enhanced this capability, allowing for more precise and efficient analyses. This technology employs a sophisticated annotation tool to label various features in the images, such as forests, bodies of water, and urban areas, making it easier to track changes over time and assess the impact of human activities on natural resources.
Understanding Annotated Satellite Imagery
Annotated satellite imagery involves the use of specific annotation tools to add descriptive information directly onto satellite photos. This process helps in identifying and categorizing physical land covers and other visible features. The annotation tool plays a crucial role in this process by enhancing the imagery with labels that can include data on vegetation types, soil conditions, water variations, and other ecological indicators.
The Role of the Annotation Tool
The primary function of the annotation tool in environmental monitoring is to provide a clear, detailed view of the landscape. Unlike traditional satellite images, annotated imagery offers a layer of interpretation that aids in comprehending the geographical and ecological constructs of the area. For example, scientists can use these tools to delineate areas affected by deforestation, track the expansion of urban environments, or monitor the health of coral reefs and other marine ecosystems.
The annotation tool typically includes features that allow users to outline specific areas with polygons, add text to clarify details, and categorize land use with unique color codes. Advanced tools also integrate artificial intelligence to automate some of the labeling processes, thereby speeding up the analysis and increasing its accuracy.
Applications in Environmental Monitoring
Climate Change Studies
Annotated satellite imagery is indispensable in the study of climate change. It provides empirical data that helps in observing the changes in vegetation patterns, ice cap movements, and sea level rise. By tracking these parameters over successive images, researchers can compile time series analyses that are vital for climate modeling and predicting future environmental conditions.
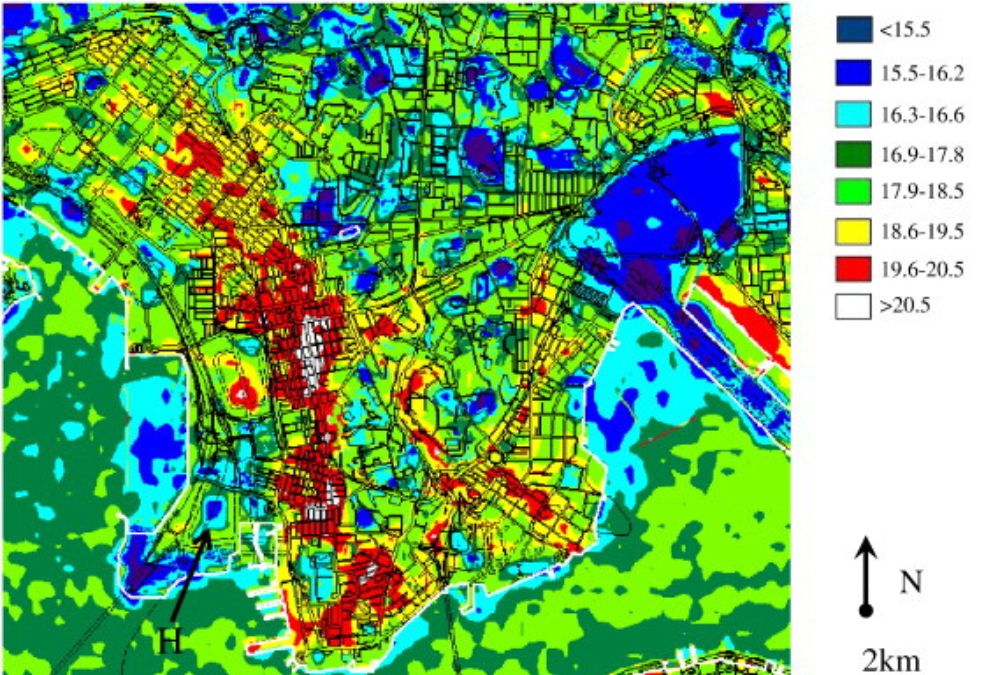
Disaster Management and Response
In the event of natural disasters such as floods, wildfires, or hurricanes, annotated satellite imagery becomes a critical tool for emergency management and recovery efforts. Rapid annotation of images can help identify the hardest-hit areas, the extent of damage, and the most effective routes for deploying aid and resources.
Urban Planning
Planners and environmentalists use annotated satellite imagery to plan sustainable expansion as metropolitan areas increase. Monitoring urban sprawl, assessing how human activity affects natural ecosystems, and putting laws into place that guarantee a balance between development and environmental preservation are all made easier with the use of this picture.
Biodiversity Conservation:
Another significant use for annotated satellite imagery is biodiversity conservation. Conservationists can make well-informed decisions about safeguarding ecosystems against the detrimental impacts of human expansion and climate change by identifying habitats and monitoring species distribution.
Challenges and Future Directions
The usage of annotated satellite imagery has drawbacks despite its many advantages. Processing and analysing high-resolution photographs demands a large amount of storage space as well as strong processing capabilities. Both the sophistication of the annotation technology and the quality of the satellite data have a significant impact on how accurate the annotations are.
With annotations on satellite imagery, environmental monitoring appears to have a bright future. It is anticipated that advancements in satellite technology and annotation software would augment the accuracy and user-friendliness of these instruments, rendering them more widely available to a larger spectrum of users, encompassing scientists, policymakers, and the general public. The potential and applications of this technology will be further expanded by innovations like improved automation and real-time monitoring.
Conclusion
Environmental monitoring has benefited greatly from the development of satellite imagery annotated with a potent annotation tool. It provides a strategy to managing and sustaining natural resources that is scalable in addition to improving the efficacy and precision of ecological evaluations. Technology is going to be used in more and more ways as it develops, and this will be vital to the worldwide effort to comprehend and address environmental concerns.